vision
- Top
- Vision
* You can see the figure enlarged.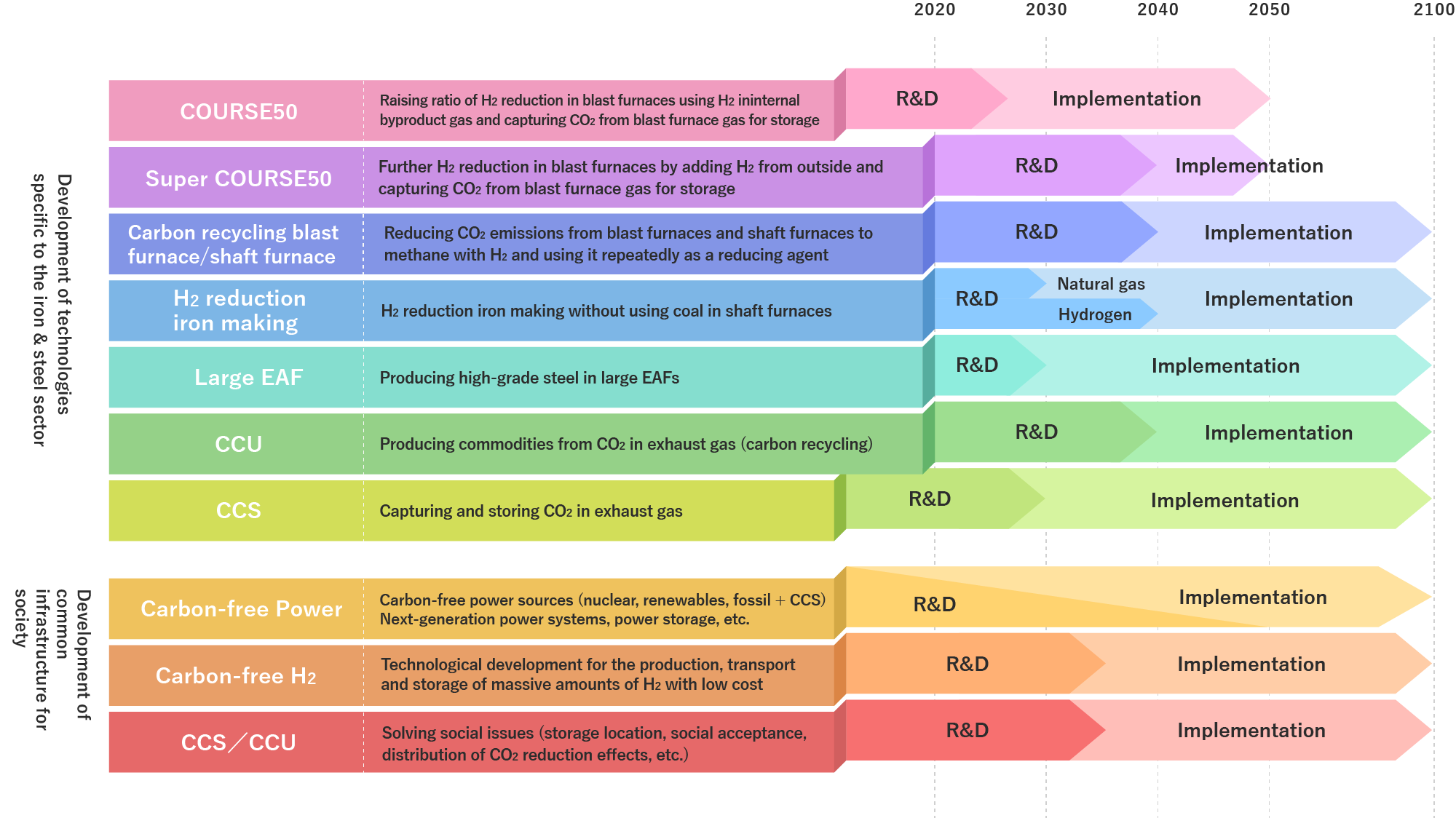
(1) COURSE50
This is technology the aim of which is to implement a technology to reduce CO2 emissions from iron and steelmaking processes by 30% or more by 2030 using H2 reduction technology and CO2 capture technology at blast furnaces using in-house H2. The technology was handed over to a GREINS project entitled “1. Development of hydrogen reduction technology using blast furnaces [1] Development of hydrogen reduction technologies utilizing hydrogen from within steelworks” in FY2021, and research and development has been carried out steadily. At the No. 2 blast furnace in the Kimitsu Area of the East Nippon Works of Nippon Steel Corporation, the company introduced a system to inject room-temperature hydrogen gas, and plans to conduct a demonstration test of the system in the second half of FY2025.(2) Super COURSE50
The Japan Iron and Steel Federation initially (in 2018) drew a roadmap setting out the move to the next step of the development of Super COURSE50, which also uses H2 from outside, after the outlook for the establishment of the COURSE50 technology improved. However, as COURSE50 is going smoothly and the social trend towards carbon neutrality is picking up speed, the research and development of Super COURSE50 was started as part of a GREINS project entitled “1. Development of hydrogen reduction technology using blast furnaces [2] Development of low-carbon technologies using external hydrogen and CO2 contained in blast furnace exhaust gas” in FY2021. Super COURSE50 is technology that injects a larger amount of H2 than COURSE50 by additionally using externally H2 purchased and to lower CO2 emissions from blast furnaces as far as possible using direct reduced iron as well.In May 2022, a test furnace in the Kimitsu Area of the East Nippon Works of Nippon Steel Corporation was remodeled and the company is conducting a test to replace part of the reducing agent of coking coal (coke) with H2. Furthermore, the goal is to demonstrate a technology to achieve a 50% or more reduction of CO2 emissions compared with the current blast furnace method by partially replacing the iron ore with direct reduced iron.
(3) Carbon recycling blast furnace
The technological development of a carbon recycling blast furnace is being carried out to capture CO2 emitted from a blast furnace and reduce it to methane with external H2 to reuse it in a blast furnace, and is to be implemented in 2050, as part of a GREINS project entitled “1. Development of hydrogen reduction technology using blast furnaces [2] Development of low-carbon technologies using external hydrogen and CO2 contained in blast furnace exhaust gas” from FY2021. At the Chiba District of the East Japan Works of JFE Steel Corporation, the company plans to build a small carbon recycling test blast furnace (150 m3-class) and verify the principle of the process through test operation from April 2025 through FY2026 to demonstrate a technology to achieve a 50% or more reduction of CO2 emissions compared with the current blast furnace method.(4) H2 reduction iron making
Regarding H2 reduction iron making, we initially (in 2018) drew a roadmap setting out the next step of Super COURSE50. However, the plan was drastically brought forward and the research and development was started in FY2021 in parallel with Super COURSE50 as a GREINS project entitled “2. Development of direct hydrogen reduction technology to reduce low-grade iron ore using only hydrogen [1] Development of direct hydrogen reduction technology to reduce low-grade iron ore using only hydrogen.”At the Hasaki Research and Development Center of Nippon Steel Corporation, the company plans to build a small test shaft furnace (1 t/hr) and start a test in FY2025 to develop direct H2 reduction technology. In addition, at the Chiba District of the East Japan Works of JFE Steel Corporation, the company plans to build a small bench test furnace and start a test in FY2024 to develop carbon recycling shaft furnace technology.
* You can see the figure enlarged.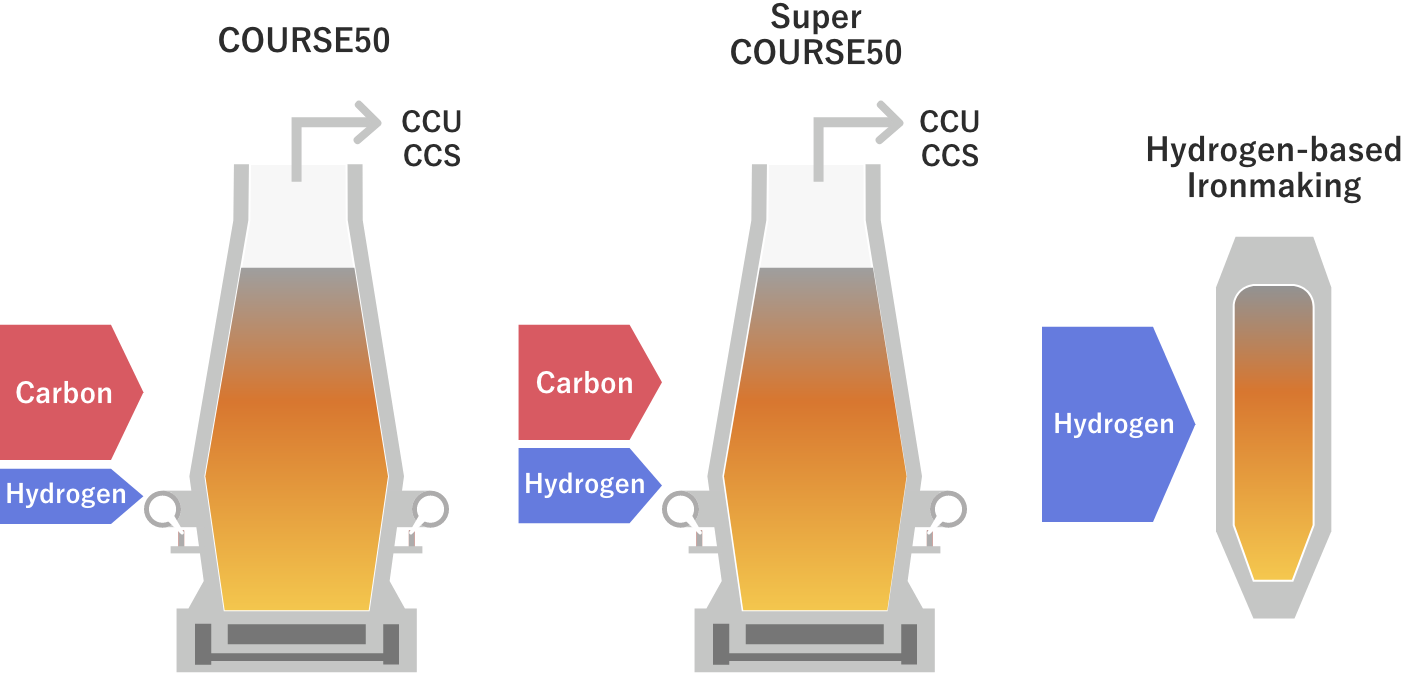
(5) Production of high-grade steel in large EAFs
Technological development was started to control the concentration of impurities as in the blast furnace method to produce high-grade steel in the H2 direct reduction furnace-EAF process in FY2021 as a GREINS project entitled “2. Development of direct hydrogen reduction technology to reduce low-grade iron ore using only hydrogen [2] Development of technology to remove impurities in electric furnaces using directly reduced iron.” This is in order to reduce CO2 emissions by overcoming technological constraints by increasing the EAF’s size to reduce the CO2 emitted in production by more than in the blast furnace method while reducing production costs to enhance competitiveness.At the Hasaki Research and Development Center of Nippon Steel Corporation, the company will build a small test EAF (10 t) and start a test in FY2024 to develop technology for the high-speed melting of reduced iron and more efficient smelting.
At the Chiba District of the East Japan Works of JFE Steel Corporation, the company will build a small test ESF (10 t) and start a test in FY2024 to develop technology for reduced iron preheating and heat provision in the furnace.
At the Takasago Works of Kobe Steel, Ltd., the company remodeled a small commercial furnace (20 t) and started a test in FY2022 to develop technology for reduced iron melting.
The challenge towards the achievement of carbon neutrality has only just begun to be taken up, and it is uncertain and difficult to predict when the goals can be achieved. However, we have agreed to the 2050 Carbon Neutral Declaration by the Japanese government and are taking on the challenge to achieve carbon neutrality in the iron and steel industry.